Latest News
First 'All-hands' Meeting
On October 18th, the first All-hands Meeting for the NSF RII award took place in Baton Rouge. As members of the RII Advisory Board, Ron Hutchins, Jordan Konisky, and Vince McCoy were present. Two of the LONI Institute fellows attended the meeting as well. You can download presentations of Drs. Allen, Cortez, Gaver, Khonsari, and Seidel. Here are pictures and a few more details on the meeting. [Other News]
Software Used in the Development of CyberTools
CyberTools will include services and tools for data-sharing, on-demand computing and dynamic scheduling, dynamic data-driven application systems, metadata catalogues and decision systems as well as portals, visualization tools and application toolkit. Initial applications driving CyberTools come from bioinformatics, computational fluid dynamics and molecular dynamics. CyberTools builds on numerous existing software projects, many of which are led by researchers in Louisiana.

|
Cactus CodeThe Cactus Framework is an open source, modular, portable, programming environment for collaborative HPC computing. The Cactus Framework allows large-scale cooperation across the globe, where individual groups design and maintain individual code modules, relying on Cactus to make these modules interoperate. |
|
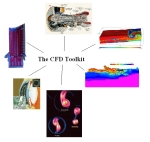
CFD ToolkitThe CFD Toolkit is an on-going research initiative at the Center for Computation & Technology (CCT), which is building a collaborative problem-solving environment for grand challenge fluid flow and transport problems. The CFD Toolkit is built using the Cactus framework and will support applications in coastal modelling, and astrophysics. |

|
Charm++Charm++ is a machine independent parallel programming system which allows programs to run unchanged on MIMD machines with or without a shared memory. Charm++ provides high-level mechanisms and strategies to facilitate the task of developing even highly complex parallel applications. |

|
Globus ToolkitThe Globus Toolkit is an open source software toolkit used for building grids. It is being developed by the Globus Alliance and many others all over the world. A growing number of projects and companies are using the Globus Toolkit to unlock the potential of grids for a wide variety of applications. |

|
GridSphereThe GridSphere portal framework provides an open-source portlet based Web portal. GridSphere enables developers to quickly develop and package third-party portlet web applications that can be run and administered within the GridSphere portlet container. |

|
HARCHARC (the Highly-Available Resource Co-allocator) is a system for reserving multiple resources in a coordinated fashion. HARC can handle multiple types of resource, and has been used to reserve time on supercomputers distributed across a US-wide testbed, together with dedicated 10 Gb/s lightpaths connecting the machines. |

|
PetaSharePetaShare will enable transparent handling of underlying data sharing, archival, and retrieval mechanisms; and will make data available to the scientists for analysis and visualization on demand. PetaShare will respond to an urgent need of scientists who are working with large data generation, sharing and collaboration requirements. |

|
SAGAThe Simple API for Grid Applications (SAGA) provides an application-level programming abstraction for distributed environments. It provides a simple and consistent programmatic interface to the most commonly required Grid functionality. SAGA is a soon to become OGF technical specification thus ensuring that it is stable, widely adopted and available. |
|
SPRUCESPRUCE is a system to support urgent or event-driven computing on both traditional supercomputers and distributed Grids. Scientists are provided with transferable Right-of-Way tokens with varying urgency levels. During an emergency, a token has to be activated at the SPRUCE portal, and jobs can then request urgent access. Local policies dictate the response, which may include providing "next-to-run" status or immediately preempting other jobs. |
StorkStork is a batch scheduler specialized in data placement and data movement, which is based on the concept and ideal of making data placement a first class entity in a distributed computing environment. Stork implements teniques specific to queueing, scheduling, and optimization of data placement jobs, and provides a level of abstraction between the user applications and the underlying data transfer and storage resources. Stork is an ongoing joint project between Louisiana State University and University of Wisconsin-Madison. |
|

|
VineVine is a modular, extensible Java library that offers developers an easy-to-use, high-level Application Programmer Interface (API) for Grid-enabling applications. Vine can be deployed for use in desktop, Java Web Start, Java Servlet and Java Portlet 1.0 environments with ease. Plus Vine supports a wide array of middleware and third-party services, so you can focus on your applications and not lose focus on the Grid! |
[ Back to top ]
